% % heat_code.m %
Code computes optimal parameters, the sensitivity matrices, and covariance matrix for the aluminum rod data analyzied in Example 7.16.
Required functions: heat_fun_al.m Required data: final_al_data.txt
clear all close all global data_al xdata % % Load the data and construct the x datapoints. % load final_al_data.txt data_al = final_al_data(2:16); xdata = [10 14 18 22 26 30 34 38 42 46 50 54 58 62 66]; xvals = [10:.1:70]; u_amb = final_al_data(17);
Input dimensions and material constants for the alumunim rod.
a = 0.95; % cm b = 0.95; % cm L = 70.0; % cm k = 2.37; % W/cm C n = 15; % Number of measurements p = 2; % Number of parameters
Optimize parameters and construct increments used when approximating sensitivities using finite differences. The representations are truncated to two significant digits to remain consistent with the measured temperatures.
h_init = 0.00183; Q_init = -15.93; q_init = [h_init Q_init]; modelfun = @(q)heat_fun_al(q,a,b,L,k,u_amb); [q_opt,fval] = fminsearch(modelfun,q_init); h = q_opt(1); Q = q_opt(2); h = 0.00191; Q = -18.41; dh = 1e-10; dQ = 1e-4; h_p = h + dh; Q_p = Q + dQ;
Construct constants and analytic solution to the steady state heat equation.
gamma = sqrt(2*(a+b)*h/(a*b*k)); gamma_h = (1/(2*h))*gamma; f1 = exp(gamma*L)*(h + k*gamma); f2 = exp(-gamma*L)*(h - k*gamma); f3 = f1/(f2 + f1); f1_h = exp(gamma*L)*(gamma_h*L*(h+k*gamma) + 1 + k*gamma_h); f2_h = exp(-gamma*L)*(-gamma_h*L*(h-k*gamma) + 1 - k*gamma_h); c1 = -Q*f3/(k*gamma); c2 = Q/(k*gamma) + c1; f4 = Q/(k*gamma*gamma); den2 = (f1+f2)^2; f3_h = (f1_h*(f1+f2) - f1*(f1_h+f2_h))/den2; c1_h = f4*gamma_h*f3 - (Q/(k*gamma))*f3_h; c2_h = -f4*gamma_h + c1_h; c1_Q = -(1/(k*gamma))*f3; c2_Q = (1/(k*gamma)) + c1_Q; gamma_hp = sqrt(2*(a+b)*h_p/(a*b*k)); f1_hp = exp(gamma_hp*L)*(h_p + k*gamma_hp); f2_hp = exp(-gamma_hp*L)*(h_p - k*gamma_hp); f3_hp = f1_hp/(f2_hp + f1_hp); c1_hp = -Q*f3_hp/(k*gamma_hp); c2_hp = Q/(k*gamma_hp) + c1_hp; c1_Qp = -Q_p*f3/(k*gamma); c2_Qp = Q_p/(k*gamma) + c1_Qp; uvals = c1*exp(-gamma*xvals) + c2*exp(gamma*xvals) + u_amb; uvals_data = c1*exp(-gamma*xdata) + c2*exp(gamma*xdata) + u_amb; uvals_Q_data = c1_Q*exp(-gamma*xdata) + c2_Q*exp(gamma*xdata); uvals_h_data = c1_h*exp(-gamma*xdata) + c2_h*exp(gamma*xdata) + gamma_h*xdata.*(-c1*exp(-gamma*xdata) + c2*exp(gamma*xdata)); uvals_data_hp = c1_hp*exp(-gamma_hp*xdata) + c2_hp*exp(gamma_hp*xdata) +u_amb; uvals_data_Qp = c1_Qp*exp(-gamma*xdata) + c2_Qp*exp(gamma*xdata) + u_amb; S_d = [ones(1,15); xdata; xdata.^2; xdata.^3; xdata.^4]; h_fd = (1/dh)*(uvals_data_hp - uvals_data); Q_fd = (1/dQ)*(uvals_data_Qp - uvals_data); res = data_al - uvals_data;
Plot the model fit and residuals.
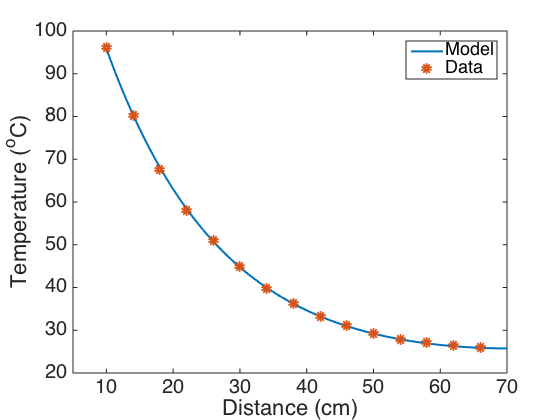
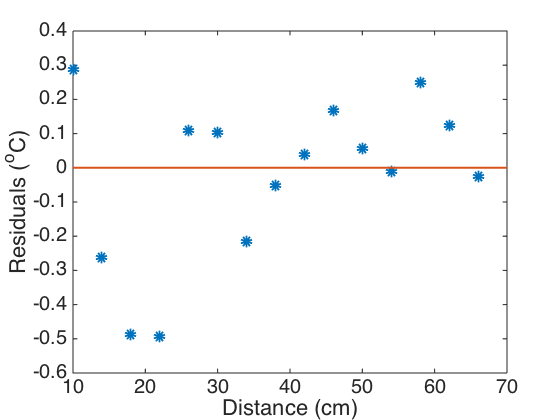
figure(1) plot(xvals,uvals,'linewidth',2) axis([5 70 20 100]) hold on plot(xdata,data_al,'o','linewidth',5) hold off set(gca,'Fontsize',[20]); xlabel('Distance (cm)') ylabel('Temperature (^oC)') legend('Model','Data','Location','Northeast') figure(2) plot(xdata,res,'o','linewidth',6) axis([10 70 -.6 .4]) hold on plot(xvals,0*xvals,'linewidth',2) hold off set(gca,'Fontsize',[20]); xlabel('Distance (cm)') ylabel('Residuals (^oC)')
Construct the analytic and finite difference sensitivity matrices.
sens_mat = [uvals_Q_data; uvals_h_data] sens_mat_fd = [Q_fd; h_fd] % % Construct the measurment covariance sigma2 and the covariance matrices % V and V_fd constructed using the analytic and finite difference % sensitivity relations. % format short e sigma2 = (1/(n-p))*res*res'; V = sigma2*inv(sens_mat*sens_mat') V_fd = sigma2*inv(sens_mat_fd*sens_mat_fd')
sens_mat = Columns 1 through 6 -4.0501e+00 -3.2100e+00 -2.5449e+00 -2.0187e+00 -1.6025e+00 -1.2738e+00 -3.1056e+04 -2.8266e+04 -2.5323e+04 -2.2416e+04 -1.9666e+04 -1.7143e+04 Columns 7 through 12 -1.0145e+00 -8.1051e-01 -6.5075e-01 -5.2648e-01 -4.3093e-01 -3.5888e-01 -1.4882e+04 -1.2897e+04 -1.1187e+04 -9.7437e+03 -8.5538e+03 -7.6028e+03 Columns 13 through 15 -3.0640e-01 -2.7063e-01 -2.4962e-01 -6.8770e+03 -6.3645e+03 -6.0561e+03 sens_mat_fd = Columns 1 through 6 -4.0501e+00 -3.2100e+00 -2.5449e+00 -2.0187e+00 -1.6025e+00 -1.2738e+00 -3.1056e+04 -2.8266e+04 -2.5323e+04 -2.2416e+04 -1.9666e+04 -1.7143e+04 Columns 7 through 12 -1.0145e+00 -8.1051e-01 -6.5075e-01 -5.2648e-01 -4.3093e-01 -3.5888e-01 -1.4882e+04 -1.2897e+04 -1.1187e+04 -9.7437e+03 -8.5538e+03 -7.6028e+03 Columns 13 through 15 -3.0640e-01 -2.7063e-01 -2.4962e-01 -6.8770e+03 -6.3644e+03 -6.0561e+03 V = 2.1034e-02 -2.0286e-06 -2.0286e-06 2.0972e-10 V_fd = 2.1034e-02 -2.0286e-06 -2.0286e-06 2.0972e-10
Construct the 95% confidence intervals.
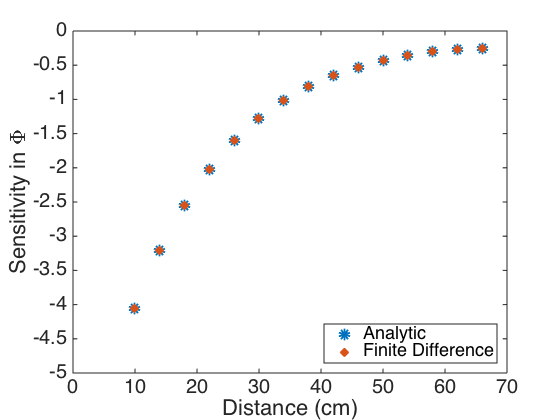
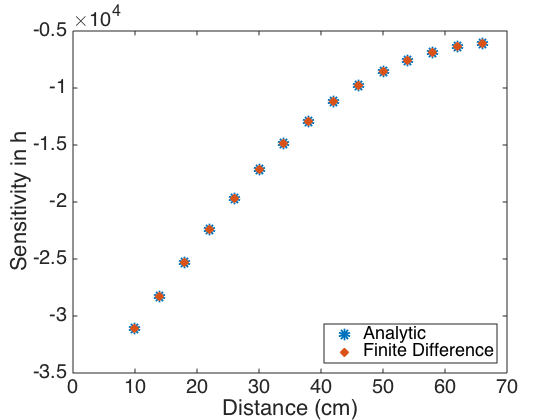
tval = 2.1604; int_Q = [Q - sqrt(V(1,1))*tval Q + sqrt(V(1,1))*tval] int_h = [h - sqrt(V(2,2))*tval h + sqrt(V(2,2))*tval] % % Plot the sensitivities obtained analytically and using finite differences % to show that to within visual accuracy, they are the same. % figure(3) plot(xdata,uvals_Q_data,'o',xdata,Q_fd,'x','linewidth',6) axis([0 70 -5 0]) set(gca,'Fontsize',[20]); xlabel('Distance (cm)') ylabel('Sensitivity in \Phi') legend('Analytic','Finite Difference','Location','Southeast') figure(4) plot(xdata,uvals_h_data,'o',xdata,h_fd,'x','linewidth',6) axis([0 70 -3.5e4 -0.5e4]) set(gca,'Fontsize',[20]); xlabel('Distance (cm)') ylabel('Sensitivity in h') legend('Analytic','Finite Difference','Location','Southeast')
int_Q = -1.8723e+01 -1.8097e+01 int_h = 1.8787e-03 1.9413e-03